Bremen (state)
The Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (German: Freie Hansestadt Bremen, pronounced [ˈbʁeːmən]) is the smallest of Germany's 16 states. A more informal name, but used in some official contexts, is Land Bremen ('State of Bremen').
Geography
The state of Bremen consists of two separated enclaves: Bremen, officially the 'City' (Stadtgemeinde Bremen) which is the state capital, and the city of Bremerhaven (Stadt Bremerhaven). Both are located on the River Weser; Bremerhaven is further downstream and serves as a North Sea harbour (the name means "Bremen's harbour"). Both cities are completely surrounded by the neighbouring State of Lower Saxony (Niedersachsen). The two cities are the only administrative subdivisions the state has.
History
At the unwinding of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806 the Free Imperial City of Bremen (as of 1646, after earlier privileges of autonomy of 1186) was not mediatised but became a sovereign state officially titled Free Hanseatic City of Bremen. In 1811 the First French Empire annexed the city-state. Upon the first, however only preliminary defeat of Napoléon Bonaparte, Bremen resumed its pre-1811 status as city-state in 1813. The Vienna Congress of 1815 confirmed Bremen's - as well as Frankfurt's, Hamburg's, and Lübeck's - independence after pressurising by Bremen's emissary, and later burgomaster, Johann Smidt. Bremen became one of 39 sovereign states of the German Confederation. In 1827 the state of Bremen bought the tract of land from the Kingdom of Hanover, where future Bremerhaven would be established. Bremen became part of the North German Confederation in 1867 and became an autonomous component state of the new-founded German Empire in 1871 and stayed with Germany in its following forms of government.
Bremen, which in 1935 had become a regular city at the de facto abolition of statehood of all component German states within the Third Reich, was reestablished as state in 1947. Being - at that time - actually located in the British Zone of Occupation the Control Commission for Germany - British Element and the Office of Military Government for Germany, U.S. (OMGUS) agreed in 1947 to constitute the cities of Bremen and then Wesermünde - in their borders altered in 1939 - as a German state named again Free Hanseatic City of Bremen, becoming at that occasion an exclave of the American Zone of Occupation within the British zone. In 1949 the city-state joined the then West German Federal Republic of Germany.
Politics
Political system
The legislature of the state of Bremen is the Bürgerschaft (citizens' assembly), elected by the citizens in the two cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven.
The executive is constituted by the Senate, elected by the Bürgerschaft. The Senate is chaired by the President of the senate (Senatspräsident), who is also one of the mayor of the city of Bremen (Bürgermeister) and is elected directly by the Bürgerschaft. The Senate selects of its members as a second mayor who serves as deputy of the president. In contrast to the Federal Chancellor of Germany or other German states, the President of the Senate has no authority to override senators on policy, which is decided upon by the senate collectively.
On a municipal level, the two cities in the state are administered separately:
- The administration of the city of Bremen is headed by the two mayors and controlled by the portion of the Bürgerschaft elected in the city of Bremen.
- Bremerhaven, on the other hand, has a municipal assembly distinct from the state legislature and an administration under a distinct head mayor (Oberbürgermeister) and a distinct second mayor.
2003 state elections
Dr. Henning Scherf (SPD) remained Mayor and Senate President, in an SPD-CDU grand coalition. As promised he resigned after half of the legislative period. The Mayor and Senate President since 8 November 2005 is Jens Böhrnsen.
| Party |
Party List votes |
Vote percentage |
Total Seats |
Seat percentage |
| Social Democratic Party (SPD) |
123,480 |
42.3% (-0,2) |
40 (-7) |
48.2% |
| Christian Democratic Union (CDU) |
86,819 |
29.8% (-7,2) |
29 (-13) |
34.9% |
| Alliance '90/The Greens |
37,350 |
12.8% (+3,8) |
12 (+2) |
14.5% |
| Free Democratic Party (FDP) |
12,294 |
4.2% (+1,7) |
1 (+1) |
1.2% |
| Deutsche Volksunion (DVU) |
6,642 |
2.3% (-0,7) |
1 (=) |
1.2% |
| Law and Order Offensive Party |
12,876 |
4.3% (+4,3) |
0 (=) |
0.0% |
| Party of Democratic Socialism (PDS) |
4,885 |
1.7% (-1,2) |
0 (=) |
0.0% |
| All Others |
7420 |
2.6% (-0,5) |
0 (=) |
0.0% |
| Totals |
291,766 |
100.0% |
83 (-17) |
100.0% |

Seat results -- SPD in red, CDU in black, Greens in green, FDP in yellow, DVU in blue
2007 state elections
The 2007 elections were held on 13 May.

Seat results -- SPD in red, CDU in black, Greens in green, FDP in yellow, The Left in purple, DVU in brown. Note: The only DVU representative, Siegfried Tittmann, left the party in July 2007 and has not joined another party.
Education
The University of Bremen is the largest university in Bremen. Furthermore Bremen has a University of the Arts Bremen, a University of Applied Sciences in Bremen and another one in Bremerhaven, and more recently the Jacobs University Bremen.
See also
- Former countries in Europe after 1815
- Bombing of Bremen in World War II
External links
References
 States of the German Confederation (1815–66) States of the German Confederation (1815–66) |
|
| Empires |
|
 |
|
| Kingdoms |
|
|
| Electorates |
Hesse
|
|
| Grand Duchies |
Baden · Hesse · Luxembourg · Mecklenburg (Schwerin · Strelitz) · Oldenburg · Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
|
|
| Duchies |
Anhalt (Bernburg1 · Dessau1 · Köthen2) · Brunswick · Holstein · Limburg3 · Nassau · Saxony (Altenburg4 · Coburg-Saalfeld5 · Coburg-Gotha4 · Gotha-Altenburg5 · Hildburghausen5 · Lauenburg · Meiningen)
|
|
| Principalities |
Hesse-Homburg · Hohenzollern (Hechingen6 · Sigmaringen6) · Liechtenstein · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Waldeck and Pyrmont
|
|
| City-states |
Bremen · Frankfurt · Hamburg · Lübeck |
|
| 1 Merged with Anhalt from 1863. 2 until 1847. 3 from 1839. 4 from 1826. 5 until 1826. 6 until 1850. |
|
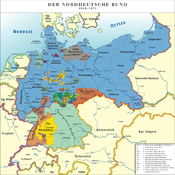
 States of the North German Confederation (1866–71) States of the North German Confederation (1866–71) |
|
| Kingdoms |
|
 |
|
| Grand Duchies |
Hesse · Mecklenburg (Schwerin · Strelitz) · Oldenburg · Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
|
|
| Duchies |
|
|
| Principalities |
Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg (Rudolstadt · Sondershausen) · Lippe · Reuss (Elder · Junior) · Waldeck-Pyrmont
|
|
| City-states |
|
|
 States of the German Empire (1871–1918) States of the German Empire (1871–1918) |
|
| Kingdoms |
|
 |
|
| Grand Duchies |
Baden · Hesse · Mecklenburg-Schwerin · Mecklenburg-Strelitz · Oldenburg · Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach
|
|
| Duchies |
Anhalt · Brunswick · Saxe-Altenburg · Saxe-Coburg and Gotha · Saxe-Lauenburg (until 1876) · Saxe-Meiningen
|
|
| Principalities |
Schaumburg-Lippe · Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt · Schwarzburg-Sondershausen · Lippe · Reuss Elder Line · Reuss Junior Line · Waldeck-Pyrmont
|
|
| City-states |
|
|
| Other territories |
|
|
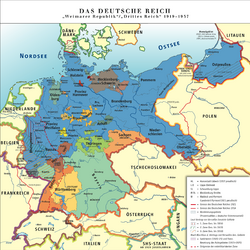
 States of Germany during the Weimar Republic (1919–33) States of Germany during the Weimar Republic (1919–33) |
|
| States |
Anhalt · Baden · Bavaria · Brunswick · Hesse · Lippe · Mecklenburg-Schwerin · Mecklenburg-Strelitz · Oldenburg · Prussia · Saxony · Schaumburg-Lippe · Thuringia (from 1920) · Waldeck (until 1929) · Württemberg
|
 |
|
| City-states |
|
|
| Until 1920 |
|
|
Altenburg · Coburg–Gotha · Meiningen · Weimar-Eisenach
|
|
|
Reuss
|
Elder · Junior
|
|
|
Schwarzburg
|
Rudolstadt · Sondershausen
|
|
|
| Unofficial |
|
|